品质至上,客户至上,您的满意就是我们的目标
技术文章
当前位置: 首页 > 技术文章
利用Videometer多光谱成像系统研究麻风树种子品质
发表时间:2021-02-02 09:28:42点击:1059
来源:北京博普特科技有限公司
分享:
来自奥胡斯大学的Birte Boelt教授和丹麦Videometer公司的Michael在知名期刊Plant Methods发表了题为Multispectral and X-ray images for characterization of Jatropha curcas L. seed quality的文章,提出了一种新型的基于多光谱成像技术和X光成像技术来进行种子品质检测组合技术。
博普特代理的VideometerLab 4多光谱成像系统和Fraunhofer植物计算机断层扫描系统同时进行种子表型和结构研究。
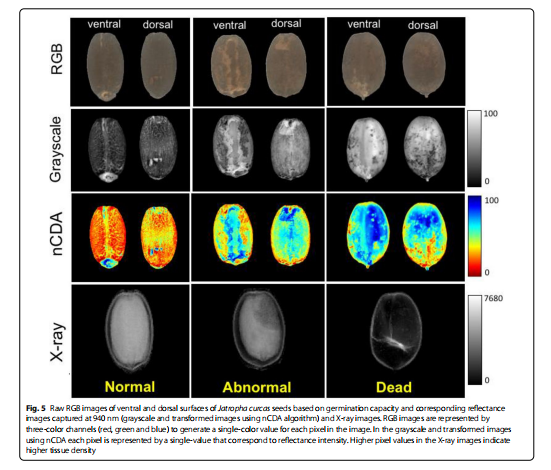
关于多光谱成像系统的使用如下
Multispectral imaging
Multispectral images were obtained using a VideometerLab4 (Videometer A/S, Herlev, Denmark) and its software VideometerLab version 3.14.9. This instrument is integrated with a sphere providing homogeneous and difuse illumination using strobe light-emitting diode (LED) technology. Refectance images were captured at 19 diferent wavelengths (365, 405, 430, 450, 470, 490, 515, 540, 570, 590, 630, 645, 660, 690, 780, 850, 880, 940 and 970 nm),combining them into high-resolution multispectral images (40 μm/pixel). Every pixel in the image contains refectance data, which varies depending on color, texture and chemical composition of the sample...
Multispectral and X-ray images for characterization of Jatropha curcas L. seed quality
· Vitor de Jesus Martins Bianchini,
· Gabriel Moura Mascarin,
· Lúcia Cristina Aparecida Santos Silva,
· Valter Arthur,
· Jens Michael Carstensen,
· Birte Boelt &
· Clíssia Barboza da Silva
Abstract
Background
The use of non-destructive methods with less human interference is of great interest in agricultural industry and crop breeding. Modern imaging technologies enable the automatic visualization of multi-parameter for characterization of biological samples, reducing subjectivity and optimizing the analysis process. Furthermore, the combination of two or more imaging techniques has contributed to discovering new physicochemical tools and interpreting datasets in real time.
Results
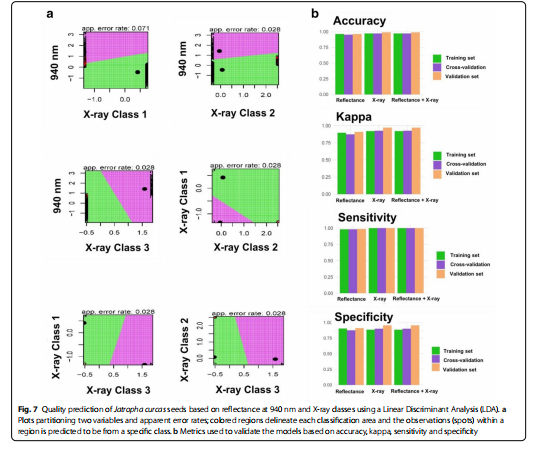
We present a new method for automatic characterization of seed quality based on the combination of multispectral and X-ray imaging technologies. We proposed an approach using X-ray images to investigate internal tissues because seed surface profile can be negatively affected, but without reaching important internal regions of seeds. An oilseed plant (Jatropha curcas) was used as a model species, which also serves as a multi-purposed crop of economic importance worldwide. Our studies included the application of a normalized canonical discriminant analyses (nCDA) algorithm as a supervised transformation building method to obtain spatial and spectral patterns on different seedlots. We developed classification models using reflectance data and X-ray classes based on linear discriminant analysis (LDA). The classification models, individually or combined, showed high accuracy (> 0.96) using reflectance at 940 nm and X-ray data to predict quality traits such as normal seedlings, abnormal seedlings and dead seeds.
Conclusions
Multispectral and X-ray imaging have a strong relationship with seed physiological performance. Reflectance at 940 nm and X-ray data can efficiently predict seed quality attributes. These techniques can be alternative methods for rapid, efficient, sustainable and non-destructive characterization of seed quality in the future, overcoming the intrinsic subjectivity of the conventional seed quality analysis.