品质至上,客户至上,您的满意就是我们的目标
技术文章
当前位置: 首页 > 技术文章
利用WIWAM XY植物表型成像系统发表鉴别新型罗替血红蛋白类似物文章
发表时间:2021-08-27 09:22:44点击:938
来源:北京博普特科技有限公司
分享:
WIWAM植物表型成像系统由比利时SMO公司与Ghent大学VIB研究所研制生产,整合了LED植物智能培养、自动 化控制系统、叶绿素荧光成像测量分析、植物热成像分析、植物近红外成像分析、植物高光谱分析、植物多光谱分 析、植物CT断层扫描分析、自动条码识别管理、RGB真彩3D成像等多项先进技术,以较优化的方式实现大量植物样 品——从拟南芥、玉米到各种其它植物的生理生态与形态结构成像分析,用于高通量植物表型成像分析测量、植 物胁迫响应成像分析测量、植物生长分析测量、生态毒理学研究、性状识别及植物生理生态分析研究等。

摘要
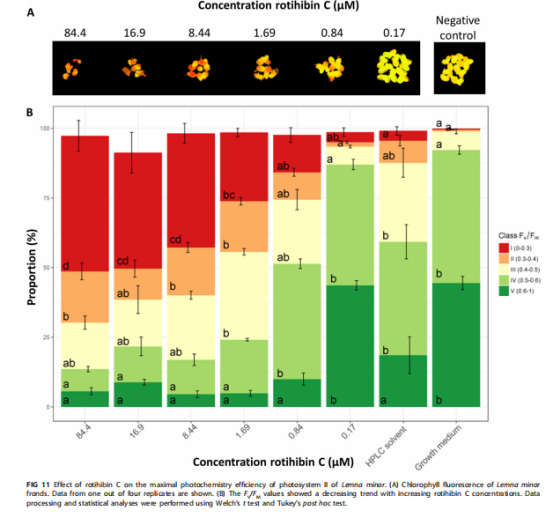
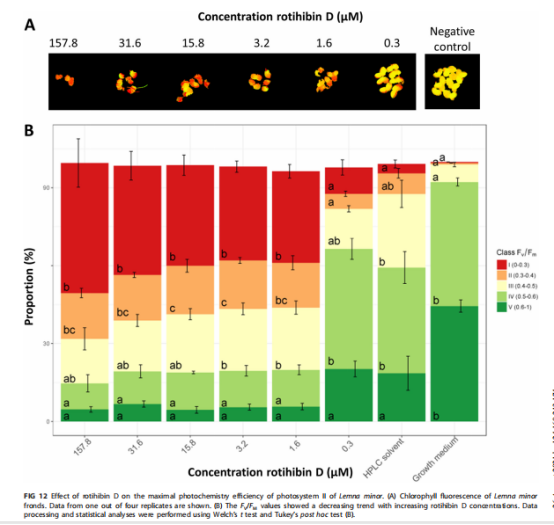
疥链霉菌是一种与常见疥痂相关的植物病原菌。这主要归因于它能够产生植物毒素thaxtomin A,其生物合成由纤维二糖触发。在对纤维二糖存在时释放的其他代谢物的调查中,我们在含有疥链霉菌的thaxtomin提取物中发现了其他化合物。质谱(MS)和核磁共振(NMR)结构分析表明,这些化合物是TOR(雷帕霉素靶点)激酶(TORK)途径抑制性脂肽rotihibin A的氨基酸序列变体,主要化合物命名为rotihibin C和D。与thaxtomin相反,在葡萄糖存在的情况下也能诱导产生Rotihibin C和D,这表明它们的生物合成受到不同的调节。通过shotgun法和靶向蛋白质组学的结合,S. scabies 87-22. 簇跨越33 kbp,编码2种不同的非核糖体肽合成酶(NRPSs)和12种附加酶。在其他公开获得的完整放线菌基因组中发现了同源rth生物合成基因簇。Rotihibins C和D在低浓度下对小柠檬和拟南芥具有除草活性,这可以通过监测对生长的影响和光系统II的最大光化学效率来证明。Rotihibins A和B是作用于TORK途径的植物生长抑制剂。研究报告了从疥链霉菌中分离和鉴定新的罗地血红蛋白序列类似物,这是马铃薯和其他块茎和根类蔬菜中常见疥痂的主要原因。通过结合蛋白质组学数据和基因组分析,发现了一个神秘的生物合成基因簇,编码能够产生罗替血红蛋白的酶机制。这项工作协助实现通过生物技术生产该脂肽变体,以研究其在拟南芥中靶向植物TORK途径的确切机制。此外,生物信息学揭示了与植物相关的链霉菌菌株中存在其他变体,包括致病性和非致病性菌株,这提出了关于这种脂肽实际功能的新问题。在非核糖体肽合成酶(NRPS)中发现一个模块,该模块包含异常瓜氨酸残基,这可能改进对由隐蔽的NRPS基因簇编码的肽的预测。
Microbiol Spectr
2021 Aug 4;e0057121.
doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00571-21. Online ahead of print.
Identification of Novel Rotihibin Analogues in Streptomyces scabies, Including Discovery of Its Biosynthetic Gene Cluster
Sören Planckaert 1, Benoit Deflandre 2, Anne-Mare de Vries 3, Maarten Ameye 4, José C Martins 3, Kris Audenaert 4, Sébastien Rigali 2, Bart Devreese 1
Affiliations expand
PMID:34346752
DOI:10.1128/Spectrum.00571-21
Abstract
Streptomyces scabies is a phytopathogen associated with common scab disease. This is mainly attributed to its ability to produce the phytotoxin thaxtomin A, the biosynthesis of which is triggered by cellobiose. During a survey of other metabolites released in the presence of cellobiose, we discovered additional compounds in the thaxtomin-containing extract from Streptomyces scabies. Structural analysis by mass spectrometry (MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) revealed that these compounds are amino acid sequence variants of the TOR (target of rapamycin) kinase (TORK) pathway-inhibitory lipopeptide rotihibin A, and the main compounds were named rotihibins C and D. In contrast to thaxtomin, the production of rotihibins C and D was also elicited in the presence of glucose, indicating different regulation of their biosynthesis. Through a combination of shotgun and targeted proteomics, the putative rotihibin biosynthetic gene cluster rth was identified in the publicly available genome of S. scabies 87-22. This cluster spans 33 kbp and encodes 2 different nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs) and 12 additional enzymes. Homologous rth biosynthetic gene clusters were found in other publicly available and complete actinomycete genomes. Rotihibins C and D display herbicidal activity against Lemna minor and Arabidopsis thaliana at low concentrations, shown by monitoring the effects on growth and the maximal photochemistry efficiency of photosystem II. IMPORTANCE Rotihibins A and B are plant growth inhibitors acting on the TORK pathway. We report the isolation and characterization of new sequence analogues of rotihibin from Streptomyces scabies, a major cause of common scab in potato and other tuber and root vegetables. By combining proteomics data with genomic analysis, we found a cryptic biosynthetic gene cluster coding for enzyme machinery capable of rotihibin production. This work may lead to the biotechnological production of variants of this lipopeptide to investigate the exact mechanism by which it can target the plant TORK pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana. In addition, bioinformatics revealed the existence of other variants in plant-associated Streptomyces strains, both pathogenic and nonpathogenic species, raising new questions about the actual function of this lipopeptide. The discovery of a module in the nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) that incorporates the unusual citrulline residue may improve the prediction of peptides encoded by cryptic NRPS gene clusters.
Keywords: Streptomyces; TORK; common scab; lipopeptide; nonribosomal peptide; proteomics.