品质至上,客户至上,您的满意就是我们的目标
当前位置: 首页 > 新闻动态
科学家联用Plantarray系统与太阳诱导叶绿素荧光(SIF)研究胁迫条件下光合作用
发表时间: 点击:650
来源:北京博普特科技有限公司
分享:
来自以色列的科学家联用Plantarray系统与太阳诱导叶绿素荧光(SIF),发表了题“Limitations of Solar-Induced Chlorophyll Fluorescence (SIF) for Estimating Photosynthesis Under Stress”的文章,文章摘要收录于NAPPN Annual Conference Abstract。
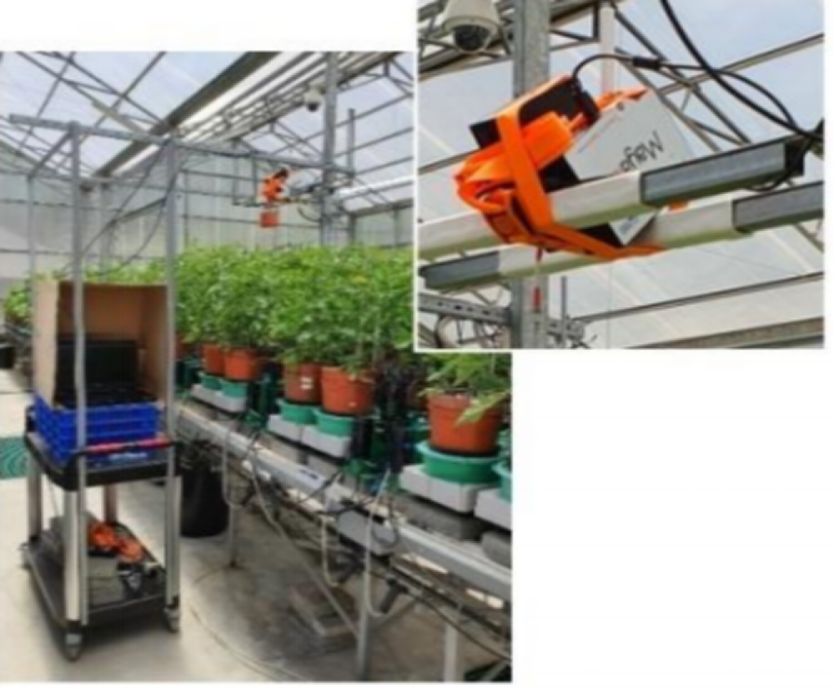

摘要
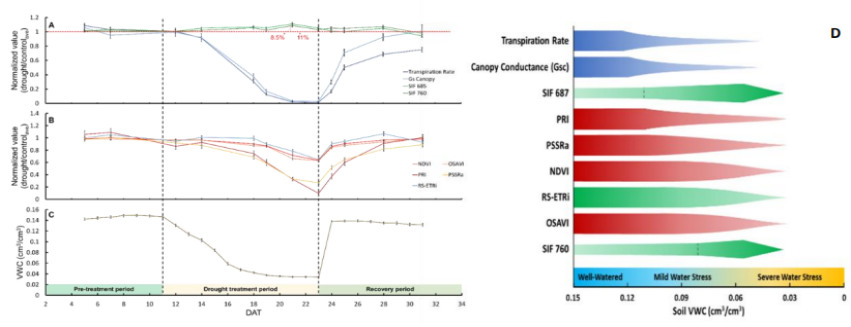
在各种条件下生长的植物光合作用的高通量测量可能为植物光合性能的可塑性研究提供重要见解。光合活性遥感[即太阳诱导的叶绿素荧光(SIF)]及其衍生物是下一代遥感技术,能够在野外条件下进行高通量的光合作用测量。我们假设,通过在标准化的受控干旱实验中同时测量SIF和整个植物的水分关系,将能够量化光合活性,并在早期检测水分胁迫。应用功能表型平台(Plantarray)进行干旱控制处理,并监测番茄渗入系(IL)的生长和水分平衡。在非胁迫条件下,一个新的SIF衍生指数——电子传输速率(RS ETRi)与全植物气孔导度(Gsc)呈负相关;而在干旱胁迫下,这些因素之间存在正相关。SIF与植物生物量或Gsc之间没有显著关系。SIF 687对干旱的响应比任何其他测量的植被指数(VI)都早。SIF参数不能区分IL系;而ILs之间的差异通过重量-水关系测量清楚地识别。我们得出结论,SIF在检测ILs之间的生理差异方面没有提供任何优于常用方法的优势。总的来说,尽管SIF在光合作用中起着重要作用,但SIF与光合作用之间的关系是复杂的,我们认为使用SIF来量化光合活性是过于简单的。
Limitations of Solar-Induced Chlorophyll Fluorescence (SIF) for Estimating Photosynthesis Under Stress
Abstract
High-throughput measurements of photosynthesis of plants grown under various conditions may provide important insights into the plasticity of the photosynthetic performance of plants. Remote sensing of photosynthetic activity [i.e., solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence (SIF)] and its derivatives are the next generation of remote techniques, enabling high-throughput photosynthesis measurements under field conditions. We hypothesized that by measuring SIF simultaneously with measurements of whole-plant water relations in a standardized controlled drought experiment, we would be able to quantify photosynthetic activity and to detect water stress at an early stage. A functional-phenotyping platform was used to apply the controlled drought treatment and to monitor the growth and water balance of tomato introgression lines (ILs). A new SIF-derived index, electron transport rate (RS-ETRi), was found to be negatively correlated with whole-plant stomatal conductance (Gsc) under non-stressed conditions; whereas a positive correlation was observed between those factors under drought stress. No significant relationships were found between SIF and plant biomass or Gsc. SIF 687 responded to drought earlier than any of the other measured vegetation indices (VIs). SIF parameters could not differentiate between IL lines; whereas differences between ILs were clearly identified by the gravimetric water-relations measurements. We concluded that SIF did not provide any advantage over commonly used methods for detecting physiological differences between the ILs. Overall, although SIF plays a significant role in photosynthesis, the relationship between SIF and photosynthesis is complex and we believe it would be an oversimplification to use SIF to quantify photosynthetic activity.