品质至上,客户至上,您的满意就是我们的目标
技术文章
当前位置: 首页 > 技术文章
WIWAM室内高通量植物表型成像系统:高光谱成像预测草豆科复合栽培的产量和氮含量
发表时间:2022-10-20 15:15:23点击:769
来源:北京博普特科技有限公司
分享:
WIWAM植物表型成像系统由比利时SMO公司与Ghent大学VIB研究所研制生产,整合了LED植物智能培养、自动 化控制系统、叶绿素荧光成像测量分析、植物热成像分析、植物近红外成像分析、植物高光谱分析、植物多光谱分 析、植物CT断层扫描分析、自动条码识别管理、RGB真彩3D成像等多项先进技术,以较优化的方式实现大量植物样 品——从拟南芥、玉米到各种其它植物的生理生态与形态结构成像分析,用于高通量植物表型成像分析测量、植物胁迫响应成像分析测量、植物生长分析测量、生态毒理学研究、性状识别及植物生理生态分析研究等。

高光谱成像技术能否成功用于推进精准农业,在很大程度上取决于对感兴趣物种的校准。迄今为止,用于预测植物生长和养分含量的高通量高光谱成像在很大程度上仅限于单一物种的栽培。因此,本研究旨在根据高光谱图像数据校准混合栽培的一系列农艺性状。它成功地证明了高光谱成像可以预测植物特性生物量(g)、叶片氮(N)浓度(mg g⁻¹)和N产量(mg)。可见光和近红外(VNIR)以及短波红外(SWIR)的输入仅导致绿色植物在背景中出现轻微的图像误分类(0.02%),而与物种无关。经过训练的偏最小二乘回归(PLSR)模型VNIR-HH(超色调)和SWIR的误分类错误率最低,分别为3.16%和9.56%,用于草豆科植物的分类。对于草,除了N×P对N产量的影响外,实验室得出的混合效应模型与高光谱测量得出的PLSR模型之间有很好的一致性。豆类模型的一致性不如草精确,可能是因为肥料驱动的处理对测量性状的影响没有那么明确。本研究确定了影响预测氮含量和生物量的PLSR模型强度的关键波长。在受控条件下,根据混合耕作的高光谱数据对生长和养分吸收特性进行有效校准,是对改进遥感技术以在混养大田作物中更广泛应用的重要贡献。
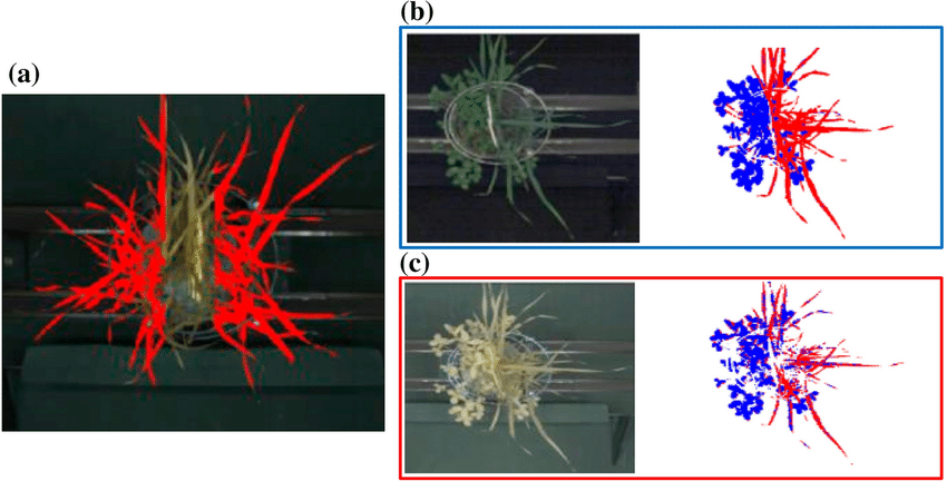

Hyperspectral imaging predicts yield and nitrogen content in grass–legume polycultures
Successful use of hyperspectral imaging technology to progress precision agriculture is highly dependent on calibration on species of interest. To date, high-throughput hyperspectral imaging to predict plant growth and nutrient content has largely been limited to single-species cultivations. Therefore, this study aimed to calibrate a range of agronomic traits in mixed cultivations to hyperspectral image data. It successfully demonstrated that hyperspectral imaging can predict the plant traits biomass (g), foliar nitrogen (N) concentration (mg g⁻¹) and N yield (mg), in grass and legume monocultures and polycultures in response to differential N and phosphorus (P) fertilization in a controlled greenhouse experiment. Visible light and near infrared (VNIR) and short wavelength infrared (SWIR) input resulted in only minor image misclassification (0.02%) for the green plants from the background regardless of species. The trained partial least square regression (PLSR) models VNIR-HH (hyper-hue) and SWIR had the lowest misclassification errors of 3.16% and 9.56% and were used for the grass–legume classification. For grass, there was good agreement between the mixed-effect models derived from the laboratory, and the PLSR models from hyperspectral measurements, except for the effect of N × P on N yield. Legume model agreement was not as precise as grass, likely because fertilizer-driven treatment effects on the measured traits were not as clear. Key wavelengths contributing to the strength of the PLSR models for predicting N content and biomass were identified from this study. Effective calibration of growth and nutrient uptake traits against hyperspectral data in mixed cultivations under controlled conditions is an important contribution towards improving remote sensing technologies for broader application in polyculture field cropping.
相关阅读
WIWAM高通量植物表型组学、植物表型成像、种质资源研究系统-玉米研究
WIWAM高通量植物表型组学、植物表型成像、种质资源研究系统-水稻线虫
WIWAM高通量植物表型组学成像分析-拟南芥的全基因关联图谱
WIWAM高通量植物表型组学成像研究—拟南芥和玉米转基因品系的功能分析
WIWAM高通量植物表型组学成像分析-轻度干旱条件下生长反应的遗传结构
WIWAM高通量植物表型组学成像研究—轻度干旱胁迫的叶片响应
WIWAM植物表型分析平台—光照和植物几何形状对叶片反射光谱的影响
WIWAM高通量植物表型平台应用—干旱胁迫下拟南芥的存活和生长研究
WIWAM高通量植物表型组学成像平台—机器人技术在表型研究中的应用
WIWAM植物表型成像系统:通过训练数据的类相关采样改进植物表型的点云分割以对抗类不平衡