品质至上,客户至上,您的满意就是我们的目标
应用案例
当前位置: 首页 > 应用案例
WIWAM叶绿素荧光成像模块-藻类应用案例
发表时间:2022-03-24 10:40:29点击:1447
来源:北京博普特科技有限公司
分享:
WIWAM植物表型成像系统由比利时SMO公司与Ghent大学VIB研究所研制生产,整合了LED植物智能培养、自动化控制系统、叶绿素荧光成像测量分析、植物热成像分析、植物近红外成像分析、植物高光谱分析、植物多光谱分析、植物CT断层扫描分析、自动条码识别管理、RGB真3D成像等多项先进技术,以优化的方式实现大量植物样品以优化的方式实现大量植物样品——从拟南芥、水稻、玉米到各种其它植物的生理生态与形态结构成像分析,用于高通量植物表型成像分析测量、植物胁迫响应成像分析测量、植物生长分析测量、生态毒理学研究、性状识别及植物生理生态分析研究等。

系统集成的叶绿素荧光成像模块使用了高分辨率图像在可控条件下对植物进行表型成像。该系统配备有相机系统以及各种光学滤波轮,有广泛用途,例如测量叶绿素荧光、红色荧光蛋白、绿色荧光蛋白、自荧光、RGB改进花青素反射指数以及叶绿素指数等。系统为自动系统,用于测量植物或植物部分的生物或非生物胁迫。
叶绿素荧光成像模块特点
组合了RGB, 叶绿素荧光、花青素、NIR和GFP/RFP图像处理,对生物和非生物胁迫的影响进行成像。这些相机也可为研究人员采集植物科学相关信息,另外还可对表型特征可视化。
系统能测量的最重要参数是Fv/FM值。该值通过叶绿素荧光获取,是指示测量植物光合性能的参数。荧光可用于测量PSII光合作用中的多种参数如线性电子流,CO2同化以及变化。
通过异源表达沼泽铜硫酯酶FatB1在海洋小绿藻中积累中链脂肪酸
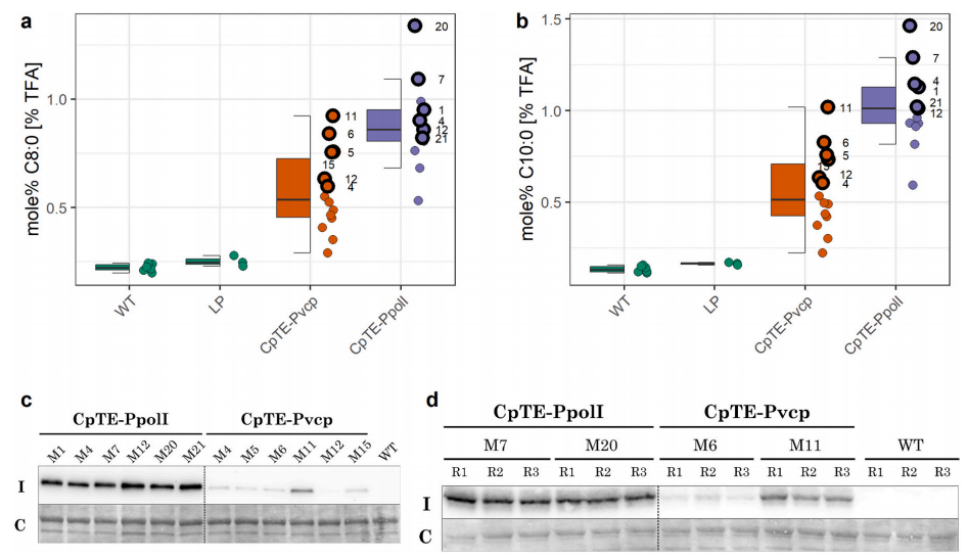
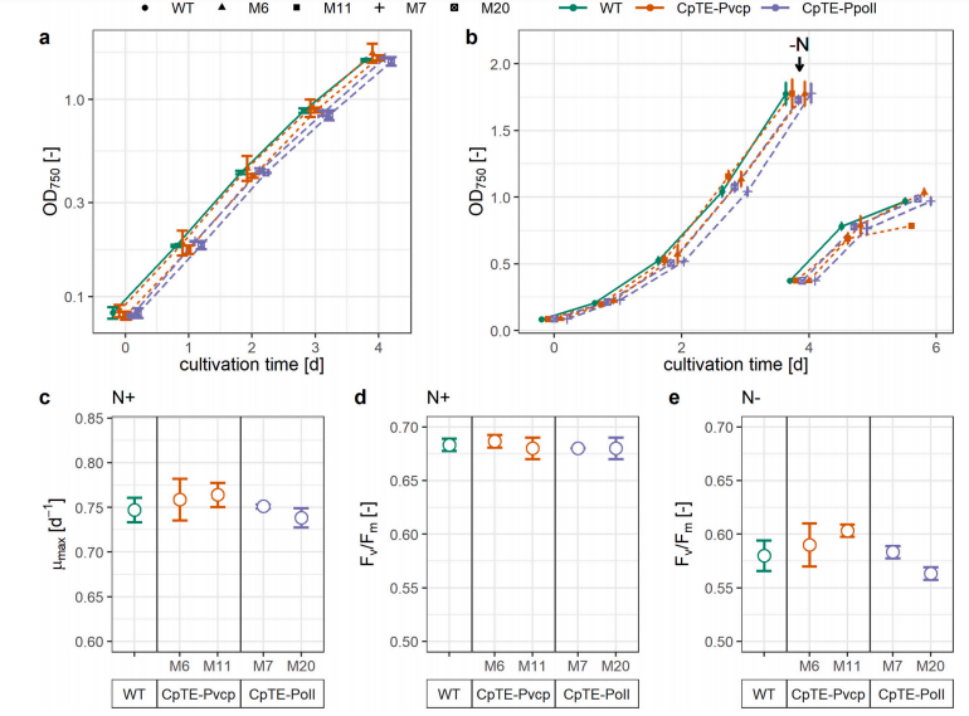
中链脂肪酸(MCFA)是一种具有相当商业价值的化合物,可用于食品、饲料和工业相关化学品的生产。由于其抗病和促进健康的作用,进一步讨论可作为疾病治疗和感染预防和控制的潜在治疗剂。能够在温带气候下生长的驯化农作物缺乏MCFA,而油棕等富含MCFA的热带物种的种植增加与森林砍伐和生物多样性减少有关。更多可持续生产的MCFA的替代来源是非驯化植物,如萼距花属(Cuphea spp.)植物,以及油料作物和含油微藻,可以通过基因工程从MCFA生产植物中表达酰基-酰基载体蛋白硫酯酶(TE)来积累MCFA。在这里,我们报告了在工业相关微藻海洋微绿球藻中,来自沼泽铜藻的TE的异源表达。使用最近开发的基因表达系统,设计了转化株,它们在贮藏脂质中分别累积了2.84%和4.15%的C8:0和C10:0,并且观察到对生长没有影响。研究进一步表明,MCFA的积累与总中性脂质含量呈负相关,表明存在限制微绿球藻中MCFA积累的调节机制
Accumulation of medium chain fatty acids in Nannochloropsis oceanica by heterologous expression of Cuphea palustris thioesterase FatB1
Abstract
Medium chain fatty acids (MCFAs) are compounds of considerable commercial interest that have applications in food, feed, and the production of industrially relevant chemicals. Due to their antipathogenic and health-promoting effects, they are further discussed as potential therapeutic agents for disease treatment and infection prevention and control. Domesticated agricultural crops that can grow in temperate climates lack MCFAs, and increased cultivation of tropical MCFA-rich species such as oil palm is associated with deforestation and a decrease in biodiversity. Alternative sources for more sustainably produced MCFAs are non-domesticated plants such as Cuphea spp., as well as oil crops and oleaginous microalgae that can be genetically engineered to accumulate MCFAs by expression of acyl-acyl carrier protein thioesterases (TEs) from MCFA-producing plants. Here, we report the heterologous expression of a TE from Cuphea palustris in the industrially relevant microalga Nannochloropsis oceanica. Using a recently developed gene expression system, we engineered transformant strains that accumulated up to 2.84 and 4.15% of C8:0 and C10:0 in storage lipids, respectively, and we observed no effect on growth. We further show that MCFA accumulation was negatively correlated with total neutral lipid content, suggesting the presence of regulatory mechanisms that limit MCFA accumulation in Nannochloropsis.