品质至上,客户至上,您的满意就是我们的目标
技术文章
当前位置: 首页 > 技术文章
Plantarray植物功能生理表型研究系统:大麦干旱与恢复:关键基因网络和反转录转座子反应
发表时间:2023-03-30 09:17:17点击:599
来源:北京博普特科技有限公司
分享:
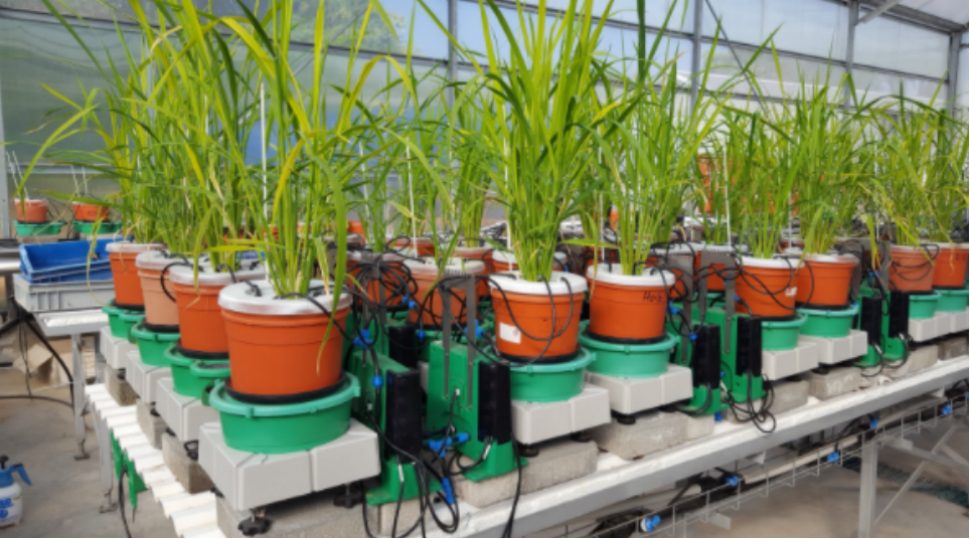

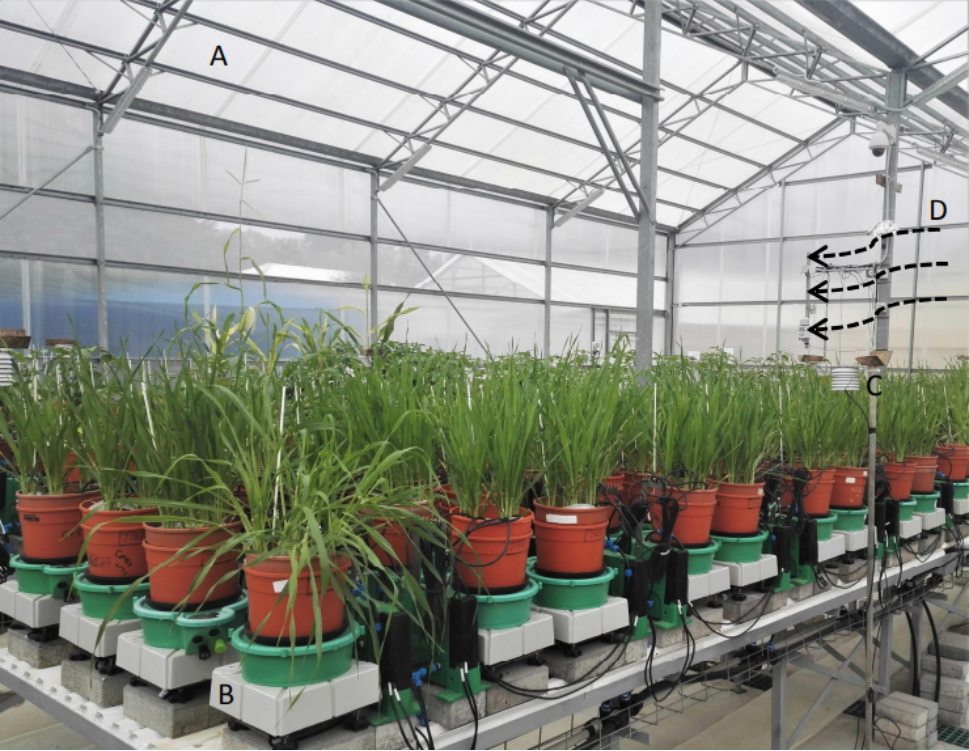
Plantarray是一款基于称重的高通量、多传感器生理表型平台以及植物逆境生物学研究通用平台。 该系统可持续、实时测量位于不同环境条件下、阵列中每个植株的土壤-植物-空气(SPAC)中的即时水流动。 直接测量根系和茎叶系统水平衡和生物量增加,计算植物生理参数以及植物对动态环境的反馈。 系统以有效、易用、无损的方式针对植物对不同处理的反应、预测植物生长和生产力进行定量比较,广泛应用于生物胁迫和非生物胁迫以及植物栽培加速育种研究等,胁迫研究涵盖干旱胁迫、盐胁迫、重金属胁迫、热、冷胁迫、光胁迫以及灌溉/养分、CO2指示、植物健康等领域的研究。
摘要
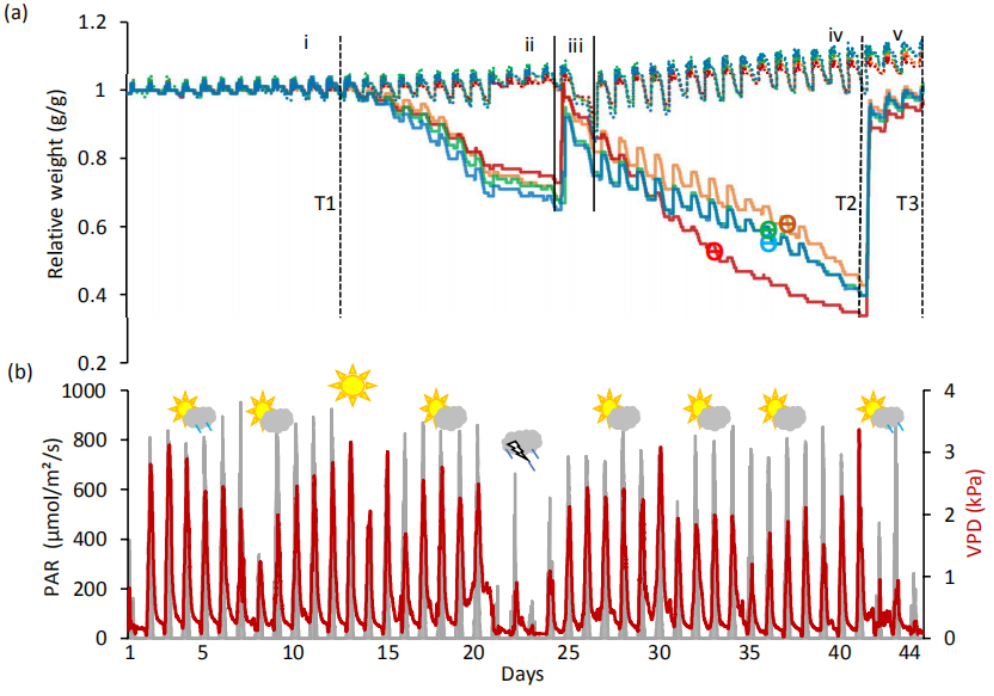
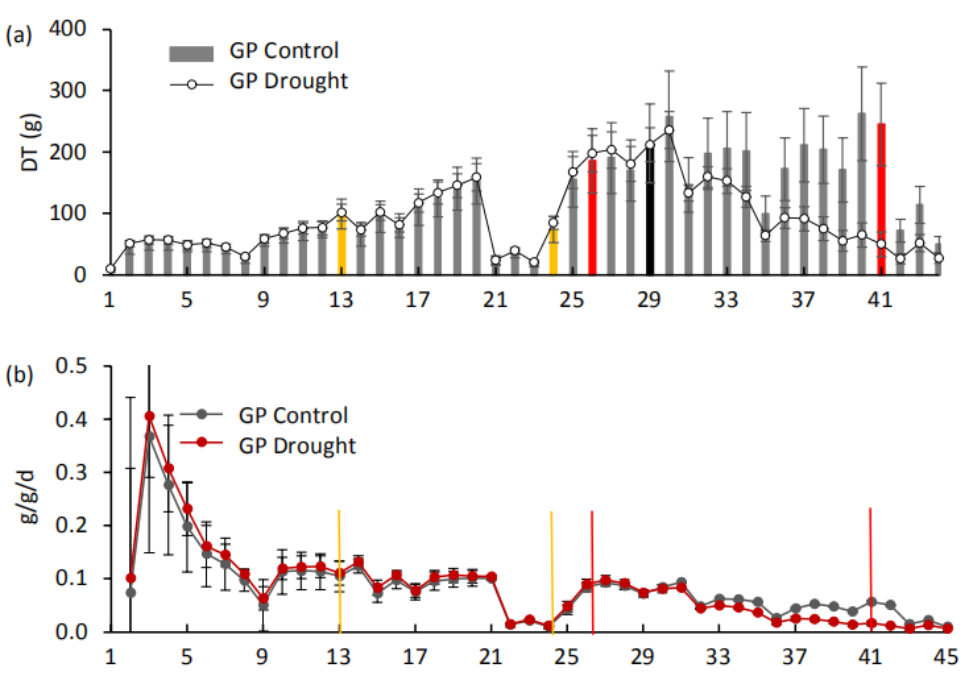
在干旱期间,植物在临界土壤含水量(SWC)下关闭气孔,同时产生不同的生理、发育和生化反应。 使用精密表型分析仪,我们对四个大麦品种(Arvo、Golden Promise、Hankkija 673和Morex)进行了开花前干旱处理,并跟踪了它们的生理反应。 对于Golden Promises品种,我们在干旱前、干旱期间和恢复期间对叶片转录物进行了RNA-seq,还检测了反转录转座子BARE1的表达。 对转录数据进行了网络分析。
不同品种的关键SWC不同,Hankkija673的反应最强烈,GoldenPromise的反应最弱。 干旱期间,与干旱和盐度反应相关的途径被强烈上调; 与生长发育相关的途径被强烈下调。 在恢复过程中,生长和发育途径被上调; 共有117个参与泛素介导的自噬的网络化基因被下调。 对SWC的不同反应表明对不同降雨模式的适应。
我们在大麦中鉴定了几个早期与干旱反应无关的强差异表达基因。 BARE1转录在干旱时被强烈转录上调,而在恢复过程中被下调,这在所研究的品种之间是不相等的。 网络自噬基因的下调表明自噬在干旱反应中发挥作用; 应进一步研究其对复原力的重要性。
关键词:大麦(Hordeum vulgare L.);干旱恢复力恢复基因表达分析;BARE逆转录转座子;自噬

Drought and recovery in barley: key gene networks and retrotransposon response
SUMMARY
During drought, plants close their stomata at a critical soil water content (SWC),together with diverse physiological, developmental, and biochemical responses. Using precision-phenotyping lysimeters, we imposed pre-flowering drought on four barley varieties (Arvo, Golden Promise, Hankkija 673 and Morex and followed their physiological responses. For Golden Promise, we carried out RNA-seq on leaf transcripts before and during drought, and during recovery, also examining retrotransposon BARE1 expression. Transcriptional data were subjected to network analysis.
The varieties differed by their critical SWC, Hankkija 673 responding at the highest and Golden Promise at the lowest. Pathways connected to drought and salinity response were strongly upregulated during drought; pathways connected to growth and development were strongly downregulated. During recovery, growth and development pathways were upregulated; altogether 117 networked genes involved in ubiquitin-mediated autophagy were downregulated. The differential response to SWC suggests adaptation to distinct rainfall patterns.
We identified several strongly differentially expressed genes not earlier associated with drought response in barley. BARE1 transcription is strongly transcriptionally upregulated by drought and downregulated during recovery unequally between the investigated cultivars. The downregulation of networked autophagy genes suggests a role for autophagy in drought response; its importance to resilience should be further investigated.
Key words: Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.); drought; resilience; recovery; gene expression analysis; BARE retrotransposon; autophagy
相关阅读
Plantarray高通量植物生理表型平台和植物逆境生物学生理研究平台-烟草研究
Plantarray高通量植物生理表型平台和植物逆境生物学生理研究平台--番茄研究
Plantarray高通量植物生理表型平台和植物逆境生物学生理研究平台--番茄研究2
Plantarray高通量植物生理表型平台和植物逆境生物学生理研究平台--番茄研究3
Plantarray高通量植物生理表型平台和植物逆境生物学生理研究平台--番茄研究4
Plantarray高通量植物生理表型平台和植物逆境生物学生理研究平台--番茄研究5
Plantarray高通量植物生理表型平台和植物逆境生物学生理研究平台-西红柿研究6
Plantarray高通量植物生理表型平台和植物逆境生物学生理研究平台-拟南芥研究1
Plantarray高通量植物生理表型平台和植物逆境生物学生理研究平台--拟南芥研究2
Plantarray高通量植物生理表型平台和植物逆境生物学生理研究平台林木研究-黑松研究
Plantarray高通量植物生理表型平台和植物逆境生物学生理研究平台林木研究-杨树研究
Plantarray高通量植物生理表型平台和植物逆境生物学生理研究平台林木研究-柑橘研究
Plantarray高通量植物生理表型平台和植物逆境生物学生理研究平台-辣椒研究2
Plantarray高通量植物生理表型平台和植物逆境生物学生理研究平台-辣椒研究3
Plantarray高通量植物生理表型平台和植物逆境生物学生理研究平台-辣椒研究4
Plantarray高通量植物生理表型平台和植物逆境生物学生理研究平台作物研究-大麦研究2
Plantarray高通量植物逆境生物学生理研究平台应用—产量与干旱研究
Plantarray植物功能生理表型系统:布鲁氏松、黑松及其强壮F1杂种的形态和生理特性比较
Plantarray功能生理表型系统:通过生理-转录组学功能方法了解蔬菜豆类中的水分保持与保护特性
Plantarray植物功能生理表型研究系统:光烟草表皮蜡成分对干旱期间的叶片有何作用
Plantarray植物功能生理表型研究系统:联用Plantarray与太阳诱导叶绿素荧光(SIF)研究胁迫条件下光合作用
Plantarray植物功能生理表型研究系统:保护细胞PIF4和HY5控制蒸腾活动